Resources
 Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Expand
Collapse
 Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Part of the Oxford Instruments Group
Super-resolution microscopy™
Super-resolution microscopy™, also called nasoscopy, allows observation of fluorescent samples at resolutions below the limit that the diffraction of light imposes on any optical microscope.
This limit, defined by Abbe, is at best ~200 nm laterally and ~500 nm axially, which is well above the resolution necessary to discriminate between different single molecules, or even ensemble of molecules within a cellular compartment. Super-resolution approaches, by breaking this diffraction barrier, are therefore extremely helpful for the visualization of structural organization and the quantification of dynamic processes down to the molecular level. Applications include the study of membrane nanostructure, protein aggregation, nuclear machinery, molecular architecture of cell-cell interface, and synaptic transmission.
Super-resolution techniques can be sorted into two main strategies:
These modalities differ in lateral/axial resolution and in the temporal resolution they can achieve.
SIM - Key principle
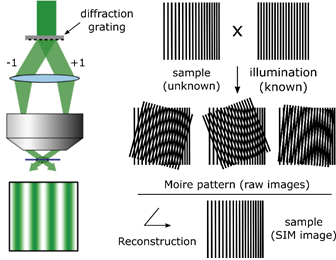
SIM relies on a laser-based wide-field microscopy set-up to which a movable diffraction grating has been inserted into the excitation beam path. Zero order and/or only first order diffracted laser beams (respectively to achieve 3D- or 2D-SIM) are allowed to pass through the objective. These laser beams interfere with each other at the focal plane of the objective and create an illumination in stripes (intensity following sinusoidal wave). This stripe pattern of light by its superimposition with the sample generates a so-called Moiré effect.
Under homogeneous illumination, the point-spread-function of the objective means that objects separated by a small distance, or in other words being organised at high frequency, are not visible. But, under structured illumination, the overlap between the high frequency organization of the objects within the sample and the high frequency of the illumination stripes creates a pattern of lower frequency which is well collected by the objective.
To reconstruct the final super-resolved image (SR-image), several raw images must be collected, each acquired at different orientation of the structured illumination. This is done by moving the diffraction grating (translation and rotation). To obtain a 2D-SIM SR-image, 9 raw images are required (3 translations x 3 rotations) and, to obtain a 3D-SIM SR-images, 15 images are required (5 translations x 3 rotations).
Note: Do not confuse this modality with non-super-resolution-SIM or optical sectioning SIM, where structured illumination is here used only to supress out-of-focus light by using only 3 sinusoidal illumination patterns (instead of 9-15) of relatively coarse stripes.
SIM - Pros and Cons
Structure illumination microscopy (SIM) allows:
However, SIM also has some drawbacks:
Andor’s Solution for SIM
Depending on how fast one needs to image and, more importantly, on how strong the fluorescence emitted from the sample, given a reasonable excitation power, both Andor iXon Life 888 EMCCD or Zyla 4.2 PLUS sCMOS are suited to SIM imaging. The table below gives a comprehensive overview of what each technology provides and the expected SIM frame rate.
If the sample supports well very short exposure times and requires extremely fast imaging at high field of view, Zyla 4.2 Plus is the recommended camera. For example, at full sensor field of view, 2D-SIM can be imaged as fast as 10 fps.
However, at short exposure times the collected signal is often weak and, in that case, it is better to opt for the most sensitive iXon Life 888 camera. Indeed, with its over 95% quantum efficiency across the visible range, combined with its negligible read noise, this camera provides the best image quality. iXon Life 888 is capable to image 2D-SIM at 10 fps as well, but with a field of view reduced to a 512 x 512 pixels sub-array, which still provides a largely sufficient field of view to image cells or subcellular dynamic events.
| Feature | iXon Life 888 | Zyla 4.2 P CamLink | Zyla 4.2 P USB 3.0 | Comments |
| Sensor size | 13.3 x 13.3 mm | 13.3 x 13.3 mm | 13.3 x 13.3 mm | Same field of view - matches well any microscope port |
| - Diagonal | 18.8 mm | 18.8 mm | 18.8 mm | iXon Life 888 has a larger photon collection area per pixel |
| - Pixel | 1024 x 1024 | 2048 x 2048 | 2048 x 2048 | Zyla 4.2 P has a higher pixel density |
| Pixel Size | 13 µm | 6.5 µm | 6.5 µm | iXon Life 888 for 100x(or higher) - Zyla 4.2 P for 60-40x |
| QE efficiency (520-640nm) | >95% | >80% | >80% | High QE + ultra low noise, iXon Life 888 is the best for sensitivity |
| Frame rate - full sensor size | 26 fps | 100 fps | 53 fps | Fastest camera frame rate using the entire sensor area |
| Exposure time/raw image | 38.5 ms | 10 ms | 18.8 ms | Resulting exposure time for a single image |
| SIM temporal res. - full sensor | 9/15 raw images to reconstruct 1 super-resolved (SR) image in 2/3D | |||
| - 2D | 346 ms (3 fps) | 90 ms (11 fps) | 170 ms (5.9 fps) | Time to acquire 1 2D-SR image and resulting frame rate |
| - 3D | 577 ms (1.7 fps) | 150 ms (6.6 fps) | 283 ms (3.5 fps) | Time to acquire 1 3D-SR image and resulting frame rate |
| Frame rate - 512 x 512 | 93 fps | 406 fps | 406 fps | Fastest camera frame rate using a sub-array (ROI) of pixels |
| Exposure time/raw image | 10.7 ms | 2.5 ms | 2.5 ms | Resulting exposure time for a single image |
| SIM temporal res. - 512 x 512 | 9/15 raw images to reconstruct 1 super-resolved (SR) image in 2/3D | |||
| - 2D | 97 ms (10 fps) | 22 ms (45 fps) | 22 ms (45 fps) | Time to acquire 1 2D-SR image and resulting frame rate |
| - 3D | 160 ms (6.3 fps) | 37.5 ms (26 fps) | 37.5 ms (26 fps) | Time to acquire 1 3D-SR image and resulting frame rate |
Learn more about Andor's Zyla 4.2 Plus and iXon Life 888 cameras.
